blog
November 26, 2025
LangChain and LangGraph and why these frameworks are becoming common in AI projects
Companies that experiment with AI soon realise that connecting an LLM with internal systems, tools and data sources is easy in a demo but difficult when a workflow needs to run reliably. Once a process becomes multi-step, interacts with external APIs or requires decisions along the way, the amount of custom glue code grows quickly.
This is where frameworks such as LangChain and LangGraph have become the common choice. They help teams shape AI workflows in a way that is easier to build, extend and maintain. That’s why many organisations across industries now rely on them when moving from a quick PoC to a serious operational tool.
What is LangChain
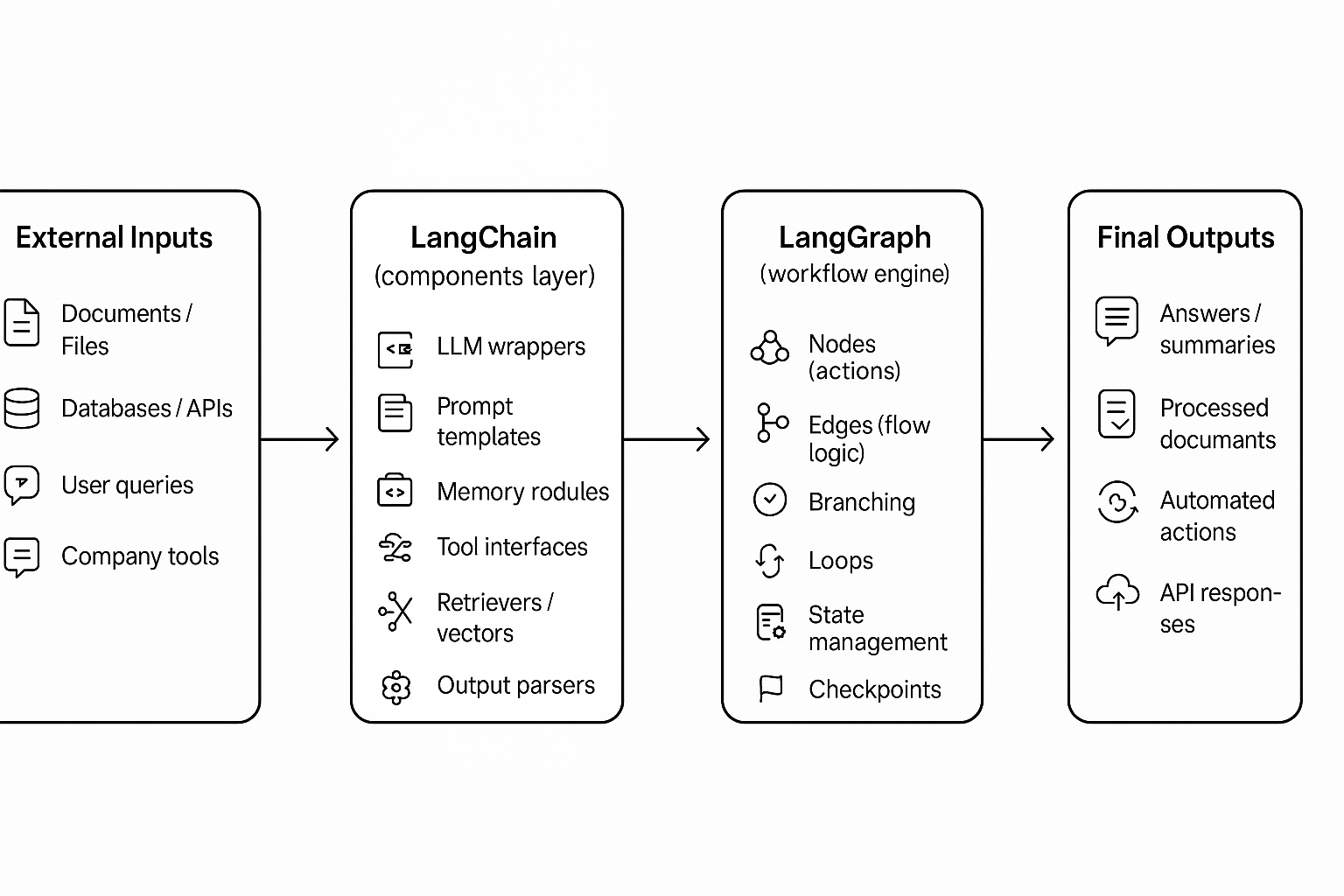
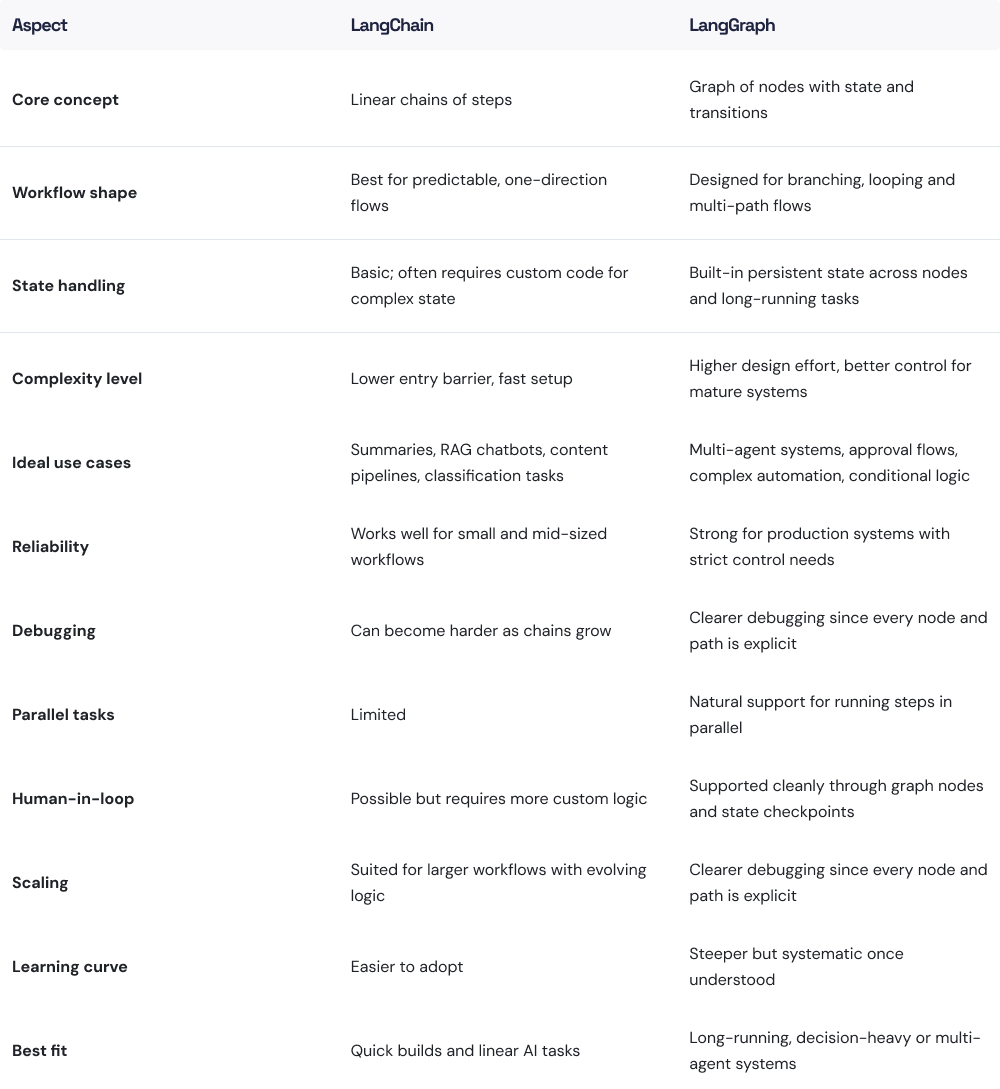
LangChain is a framework that organises AI workflows into chains — ordered sequences where each step builds on the previous one. Instead of manually wiring prompts, memory, document retrieval, parsing and tool calls, developers use ready-made components that connect smoothly.
It gives a clear structure for linear tasks: load data, prepare context, run the model, parse the result. The approach fits well when the workflow follows a predictable direction and does not need to revisit earlier steps or manage complex state.
LangChain includes modules for:
- model selection
- memory and context handling
- vector store integrations
- tool and API usage
- agents that can call these tools
- output parsers for structured results
This makes it easy to build chatbots with retrieval, content generation flows, summarisation pipelines and other step-by-step processes.
Its main limitation appears when the workflow stops being linear. If loops, conditions, repeated decisions, or multi-agent behaviour appear, the orchestration around LangChain becomes harder to maintain.
LangChain in practice
In real projects, LangChain shines when the task behaves like a clean sequence. A company that needs a summarizer for internal documents, a structured content generator, or a question-answering assistant with retrieval can build it quickly using LangChain’s components.
Developers appreciate the short setup time and the large ecosystem of integrations.
But if a project grows beyond predictable steps, the structure becomes harder to sustain. Teams often start adding custom logic around the chain to handle decisions, iterations or long-running state, and at that point LangChain’s simplicity becomes its boundary.
What is LangGraph
LangGraph is the advanced orchestration framework built inside the LangChain ecosystem, and it uses LangChain’s components to create complex, stateful workflows. It was designed for workflows that no longer behave like a straight line. Instead of chaining steps in one direction, LangGraph models the AI system as a graph with nodes, edges, and persistent state.
Nodes represent actions or agents, edges show transitions, and the framework keeps track of what the system already knows as it moves through the graph.
This model matches real business processes far better than a linear chain. Many AI workflows need to:
- loop back to previous steps
- run checks before moving on
- wait for a human decision
- call external systems multiple times
- branch into different paths
- merge results
- maintain memory across long interactions
LangGraph handles these patterns naturally and removes the need for improvised orchestration.
LangGraph in practice
Teams use LangGraph when reliability and control matter. A multi-agent workflow, a document-processing system with several approval points, or an automation pipeline that needs to revisit earlier steps will always outgrow a linear approach.
LangGraph keeps the process consistent: it manages state, handles transitions, supports retries, records what happened, and prevents the workflow from drifting into unintended behaviour.
The trade-off is that it requires more thoughtful design upfront, but once the system matures, the benefits are clear — predictable execution, easier debugging, and workflows that match the complexity of the real task.
Why teams are choosing these frameworks
Across different clients we see the same situation: a small experiment proves promising, expectations rise, and the workflow becomes more involved. What started as a simple script grows into something with many steps and decision points. That’s when the need for structure becomes obvious.
LangChain helps teams keep their linear tasks clean and quick to build, while LangGraph gives them a reliable way to manage complex behaviour without losing control. Both frameworks replace improvised orchestration with something more intentional, which explains why their adoption keeps expanding.
How Blocshop helps
Blocshop works with teams that arrive at different levels of maturity. Some bring a LangChain prototype that behaves unpredictably under load. Others arrive early and want help choosing the right framework before they commit to the design.
We help by reviewing the workflow, mapping the logic, selecting the right approach, and building a system that stays maintainable as it grows.
Blocshop supports clients with:
- workflow architecture
- state handling and agent logic
- vector store and external API integrations
- monitoring, tracing and cost control
- human-in-the-loop steps and permissions
- training for in-house teams
Many organizations prefer a gradual approach: start with LangChain to move quickly, then introduce LangGraph when the workflow becomes sophisticated. Blocshop guides this evolution safely and with minimal effort required from the client.
If you are planning a new AI system or feel your current setup is becoming difficult to maintain, Blocshop can help you build a stable foundation for your next development phase.
👉 Book a free consultation with Blocshop to review your AI workflow and choose the right approach for your roadmap.
SCHEDULE A FREE CONSULTATION
Learn more from our insights
The journey to your
custom software
solution starts here.
Services
blog
November 26, 2025
LangChain and LangGraph and why these frameworks are becoming common in AI projects
Companies that experiment with AI soon realise that connecting an LLM with internal systems, tools and data sources is easy in a demo but difficult when a workflow needs to run reliably. Once a process becomes multi-step, interacts with external APIs or requires decisions along the way, the amount of custom glue code grows quickly.
This is where frameworks such as LangChain and LangGraph have become the common choice. They help teams shape AI workflows in a way that is easier to build, extend and maintain. That’s why many organisations across industries now rely on them when moving from a quick PoC to a serious operational tool.
What is LangChain
LangChain is a framework that organises AI workflows into chains — ordered sequences where each step builds on the previous one. Instead of manually wiring prompts, memory, document retrieval, parsing and tool calls, developers use ready-made components that connect smoothly.
It gives a clear structure for linear tasks: load data, prepare context, run the model, parse the result. The approach fits well when the workflow follows a predictable direction and does not need to revisit earlier steps or manage complex state.
LangChain includes modules for:
- model selection
- memory and context handling
- vector store integrations
- tool and API usage
- agents that can call these tools
- output parsers for structured results
This makes it easy to build chatbots with retrieval, content generation flows, summarisation pipelines and other step-by-step processes.
Its main limitation appears when the workflow stops being linear. If loops, conditions, repeated decisions, or multi-agent behaviour appear, the orchestration around LangChain becomes harder to maintain.
LangChain in practice
In real projects, LangChain shines when the task behaves like a clean sequence. A company that needs a summarizer for internal documents, a structured content generator, or a question-answering assistant with retrieval can build it quickly using LangChain’s components.
Developers appreciate the short setup time and the large ecosystem of integrations.
But if a project grows beyond predictable steps, the structure becomes harder to sustain. Teams often start adding custom logic around the chain to handle decisions, iterations or long-running state, and at that point LangChain’s simplicity becomes its boundary.

What is LangGraph
LangGraph is the advanced orchestration framework built inside the LangChain ecosystem, and it uses LangChain’s components to create complex, stateful workflows. It was designed for workflows that no longer behave like a straight line. Instead of chaining steps in one direction, LangGraph models the AI system as a graph with nodes, edges, and persistent state.
Nodes represent actions or agents, edges show transitions, and the framework keeps track of what the system already knows as it moves through the graph.
This model matches real business processes far better than a linear chain. Many AI workflows need to:
- loop back to previous steps
- run checks before moving on
- wait for a human decision
- call external systems multiple times
- branch into different paths
- merge results
- maintain memory across long interactions
LangGraph handles these patterns naturally and removes the need for improvised orchestration.
LangGraph in practice
Teams use LangGraph when reliability and control matter. A multi-agent workflow, a document-processing system with several approval points, or an automation pipeline that needs to revisit earlier steps will always outgrow a linear approach.
LangGraph keeps the process consistent: it manages state, handles transitions, supports retries, records what happened, and prevents the workflow from drifting into unintended behaviour.
The trade-off is that it requires more thoughtful design upfront, but once the system matures, the benefits are clear — predictable execution, easier debugging, and workflows that match the complexity of the real task.
Why teams are choosing these frameworks
Across different clients we see the same situation: a small experiment proves promising, expectations rise, and the workflow becomes more involved. What started as a simple script grows into something with many steps and decision points. That’s when the need for structure becomes obvious.
LangChain helps teams keep their linear tasks clean and quick to build, while LangGraph gives them a reliable way to manage complex behaviour without losing control. Both frameworks replace improvised orchestration with something more intentional, which explains why their adoption keeps expanding.

How Blocshop helps
Blocshop works with teams that arrive at different levels of maturity. Some bring a LangChain prototype that behaves unpredictably under load. Others arrive early and want help choosing the right framework before they commit to the design.
We help by reviewing the workflow, mapping the logic, selecting the right approach, and building a system that stays maintainable as it grows.
Blocshop supports clients with:
- workflow architecture
- state handling and agent logic
- vector store and external API integrations
- monitoring, tracing and cost control
- human-in-the-loop steps and permissions
- training for in-house teams
Many organizations prefer a gradual approach: start with LangChain to move quickly, then introduce LangGraph when the workflow becomes sophisticated. Blocshop guides this evolution safely and with minimal effort required from the client.
If you are planning a new AI system or feel your current setup is becoming difficult to maintain, Blocshop can help you build a stable foundation for your next development phase.
👉 Book a free consultation with Blocshop to review your AI workflow and choose the right approach for your roadmap.
SCHEDULE A FREE CONSULTATION
Learn more from our insights
Let's talk!
The journey to your
custom software
solution starts here.
Services
Head Office
Revoluční 1
110 00, Prague Czech Republic
hello@blocshop.io
blog
November 26, 2025
LangChain and LangGraph and why these frameworks are becoming common in AI projects
Companies that experiment with AI soon realise that connecting an LLM with internal systems, tools and data sources is easy in a demo but difficult when a workflow needs to run reliably. Once a process becomes multi-step, interacts with external APIs or requires decisions along the way, the amount of custom glue code grows quickly.
This is where frameworks such as LangChain and LangGraph have become the common choice. They help teams shape AI workflows in a way that is easier to build, extend and maintain. That’s why many organisations across industries now rely on them when moving from a quick PoC to a serious operational tool.
What is LangChain
LangChain is a framework that organises AI workflows into chains — ordered sequences where each step builds on the previous one. Instead of manually wiring prompts, memory, document retrieval, parsing and tool calls, developers use ready-made components that connect smoothly.
It gives a clear structure for linear tasks: load data, prepare context, run the model, parse the result. The approach fits well when the workflow follows a predictable direction and does not need to revisit earlier steps or manage complex state.
LangChain includes modules for:
- model selection
- memory and context handling
- vector store integrations
- tool and API usage
- agents that can call these tools
- output parsers for structured results
This makes it easy to build chatbots with retrieval, content generation flows, summarisation pipelines and other step-by-step processes.
Its main limitation appears when the workflow stops being linear. If loops, conditions, repeated decisions, or multi-agent behaviour appear, the orchestration around LangChain becomes harder to maintain.
LangChain in practice
In real projects, LangChain shines when the task behaves like a clean sequence. A company that needs a summarizer for internal documents, a structured content generator, or a question-answering assistant with retrieval can build it quickly using LangChain’s components.
Developers appreciate the short setup time and the large ecosystem of integrations.
But if a project grows beyond predictable steps, the structure becomes harder to sustain. Teams often start adding custom logic around the chain to handle decisions, iterations or long-running state, and at that point LangChain’s simplicity becomes its boundary.

What is LangGraph
LangGraph is the advanced orchestration framework built inside the LangChain ecosystem, and it uses LangChain’s components to create complex, stateful workflows. It was designed for workflows that no longer behave like a straight line. Instead of chaining steps in one direction, LangGraph models the AI system as a graph with nodes, edges, and persistent state.
Nodes represent actions or agents, edges show transitions, and the framework keeps track of what the system already knows as it moves through the graph.
This model matches real business processes far better than a linear chain. Many AI workflows need to:
- loop back to previous steps
- run checks before moving on
- wait for a human decision
- call external systems multiple times
- branch into different paths
- merge results
- maintain memory across long interactions
LangGraph handles these patterns naturally and removes the need for improvised orchestration.
LangGraph in practice
Teams use LangGraph when reliability and control matter. A multi-agent workflow, a document-processing system with several approval points, or an automation pipeline that needs to revisit earlier steps will always outgrow a linear approach.
LangGraph keeps the process consistent: it manages state, handles transitions, supports retries, records what happened, and prevents the workflow from drifting into unintended behaviour.
The trade-off is that it requires more thoughtful design upfront, but once the system matures, the benefits are clear — predictable execution, easier debugging, and workflows that match the complexity of the real task.
Why teams are choosing these frameworks
Across different clients we see the same situation: a small experiment proves promising, expectations rise, and the workflow becomes more involved. What started as a simple script grows into something with many steps and decision points. That’s when the need for structure becomes obvious.
LangChain helps teams keep their linear tasks clean and quick to build, while LangGraph gives them a reliable way to manage complex behaviour without losing control. Both frameworks replace improvised orchestration with something more intentional, which explains why their adoption keeps expanding.

How Blocshop helps
Blocshop works with teams that arrive at different levels of maturity. Some bring a LangChain prototype that behaves unpredictably under load. Others arrive early and want help choosing the right framework before they commit to the design.
We help by reviewing the workflow, mapping the logic, selecting the right approach, and building a system that stays maintainable as it grows.
Blocshop supports clients with:
- workflow architecture
- state handling and agent logic
- vector store and external API integrations
- monitoring, tracing and cost control
- human-in-the-loop steps and permissions
- training for in-house teams
Many organizations prefer a gradual approach: start with LangChain to move quickly, then introduce LangGraph when the workflow becomes sophisticated. Blocshop guides this evolution safely and with minimal effort required from the client.
If you are planning a new AI system or feel your current setup is becoming difficult to maintain, Blocshop can help you build a stable foundation for your next development phase.
👉 Book a free consultation with Blocshop to review your AI workflow and choose the right approach for your roadmap.
SCHEDULE A FREE CONSULTATION
Learn more from our insights
Let's talk!
The journey to your
custom software solution starts here.
Services